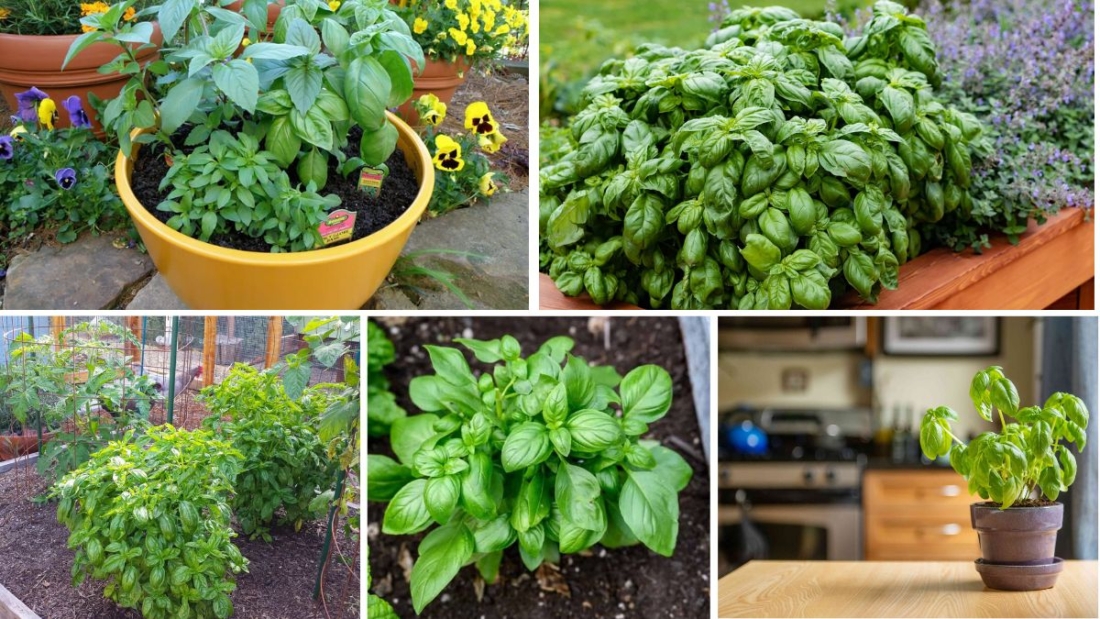
Basil (Ocimum basilicum) is a fragrant, versatile herb widely used in culinary dishes, herbal teas, and natural remedies. Known for its aromatic leaves, rich flavor, and health-promoting properties, basil has become a staple in kitchens worldwide. Indoor cultivation of basil provides fresh, readily available leaves year-round, ensures chemical-free growth, and adds greenery and pleasant aroma to indoor spaces.
This comprehensive guide offers a step-by-step approach to growing basil indoors, including selection of varieties, soil and container requirements, lighting, watering, fertilization, pruning, pest management, and harvesting techniques. It is specifically designed for beginners seeking a sustainable, rewarding indoor gardening experience.
Why Grow Basil Indoors?

Indoor cultivation of basil offers several advantages:
- Year-Round Access: Basil can thrive indoors regardless of outdoor weather conditions.
- Fresh and Healthy: Home-grown basil ensures pesticide-free, flavorful leaves.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Adds vibrant greenery and a pleasant aroma to kitchens, balconies, or living areas.
- Ease of Growth: Ideal for beginners, as basil grows relatively quickly and requires minimal maintenance.
- Herbal Benefits: Rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and essential oils that support immunity, digestion, and overall wellness.
Choosing the Right Basil Variety
There are many basil varieties, each with unique flavors, aromas, and growth habits. Choosing the right type helps optimize indoor growth:
- Sweet Basil: Classic culinary herb, ideal for Italian dishes, pesto, and salads.
- Genovese Basil: Large, aromatic leaves; preferred for authentic Italian cooking.
- Thai Basil: Distinct anise-like flavor; excellent for Asian cuisine.
- Lemon Basil: Citrus aroma and flavor; suitable for teas, salads, and desserts.
- Purple Basil: Decorative and flavorful; adds color to dishes and indoor gardens.
For indoor cultivation, compact varieties like dwarf basil or Genovese basil are ideal, as they require less space and adapt well to containers.
Selecting Containers for Indoor Basil

Proper container selection ensures healthy growth and prevents root problems:
- Size: Minimum 6–8 inches in diameter for a single plant; larger pots allow multiple plants.
- Material: Terracotta, ceramic, or plastic containers are suitable. Terracotta promotes aeration, while plastic retains moisture longer.
- Drainage: Ensure containers have sufficient drainage holes to prevent waterlogging.
- Mobility: Lightweight containers can be moved to optimize sunlight exposure.
Soil Requirements
Basil thrives in nutrient-rich, well-draining soil:
- Type: Use high-quality potting mix with organic matter or compost.
- Composition: A mix of garden soil, compost, and perlite in a 2:1:1 ratio works well.
- pH Range: Slightly acidic to neutral (6.0–7.0).
- Fertility: Supplement soil with balanced, slow-release organic fertilizers for continuous growth.
Avoid heavy clay soils that retain excess water, as basil roots are prone to rot.
Planting Basil Indoors

Basil can be grown from seeds or cuttings:
Planting from Seeds:
- Fill the container with moist, well-draining soil.
- Sow seeds ¼ inch deep and cover lightly with soil.
- Water gently to moisten the soil without displacing seeds.
- Maintain a temperature of 20–25°C (68–77°F) for optimal germination.
- Seeds germinate in 7–14 days; thin seedlings to prevent overcrowding.
Planting from Cuttings:
- Take healthy stem cuttings (4–6 inches long) from an established plant.
- Remove lower leaves to expose nodes.
- Place cuttings in water or moist soil to encourage root development.
- Transplant rooted cuttings into containers with soil.
Cuttings establish faster than seeds and ensure consistency in leaf flavor and quality.
Lighting Requirements
Basil requires ample light for strong growth and flavor:
- Sunlight: 6–8 hours of direct or bright indirect light daily.
- Artificial Lighting: Use LED grow lights or fluorescent lamps if natural sunlight is limited. Position lights 6–12 inches above plants.
- Rotation: Rotate containers every few days to ensure even light exposure and prevent leaning.
Insufficient light results in weak, leggy stems and reduced flavor.
Watering Guidelines

Basil prefers consistently moist but not waterlogged soil:
- Frequency: Water when the top inch of soil feels dry.
- Method: Water at the base to avoid wetting leaves, which can promote fungal diseases.
- Caution: Overwatering causes root rot and yellowing leaves; underwatering leads to wilting.
- Humidity: Moderate indoor humidity (40–60%) is suitable; occasional misting can help in dry environments.
Fertilization Practices
Proper nutrition enhances basil growth, flavor, and aroma:
- Type: Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer (e.g., 10:10:10) or organic options like compost tea.
- Frequency: Fertilize every 3–4 weeks during active growth.
- Avoid Over-Fertilization: Excess nitrogen promotes leaf growth but may reduce essential oils and flavor.
Pruning and Maintenance

Regular pruning encourages bushy growth, prevents flowering, and prolongs the harvest:
- Pinching Tips: Remove the top 1–2 inches of stems when plants reach 6–8 inches tall.
- Flower Removal: Prevent flowering to maintain leaf flavor; once flowers appear, leaves become bitter.
- Leaf Harvesting: Harvest leaves from the top, allowing lower leaves to continue growing.
- Cleaning: Remove yellow or damaged leaves promptly.
Pest and Disease Management
Basil is relatively resilient indoors but can encounter pests and fungal issues:
Common Pests:
- Aphids: Remove manually or spray with neem oil.
- Spider Mites: Maintain humidity and wipe leaves.
- Whiteflies: Use sticky traps or organic insecticidal sprays.
Common Diseases:
- Downy Mildew: Prevent with good air circulation and avoid wetting foliage.
- Root Rot: Caused by overwatering; ensure proper drainage.
- Fusarium Wilt: Use disease-free seeds or cuttings.
Regular inspection and preventive measures keep basil healthy and productive.
Harvesting Basil
- Timing: Begin harvesting when plants reach 6–8 inches tall.
- Method: Snip leaves above a pair of nodes using scissors or fingers.
- Frequency: Frequent harvesting encourages new growth and bushier plants.
- Storage:
- Short-term: Store leaves in a damp paper towel in the refrigerator.
- Long-term: Freeze or dry leaves for extended use.
Harvesting correctly ensures continuous supply and maintains plant vigor.
Tips for Optimal Indoor Growth
- Place basil in a sunny window or under grow lights for consistent light exposure.
- Avoid overcrowding to improve air circulation and prevent fungal problems.
- Rotate containers periodically for even growth.
- Use organic fertilizers to enhance flavor and essential oil content.
- Keep foliage dry during watering to reduce disease risk.
Health Benefits of Basil
- Antioxidant-Rich: Protects cells from oxidative damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory: Supports immune system and reduces inflammation.
- Digestive Aid: Improves digestion and reduces bloating.
- Mental Health: Aromatic compounds may reduce stress and enhance mood.
- Culinary Versatility: Enhances flavor in salads, pasta, soups, sauces, and beverages.
Conclusion
Growing basil indoors is an ideal project for beginners and seasoned gardeners alike. Its ease of care, rapid growth, aromatic leaves, and health benefits make it a valuable addition to any home. By selecting suitable varieties, providing proper soil, adequate lighting, and consistent care, basil can thrive indoors year-round.
Regular pruning, proper watering, and preventive pest management ensure healthy, flavorful plants. Indoor basil cultivation not only enhances the visual appeal and aroma of living spaces but also provides fresh, nutrient-rich leaves for culinary and medicinal uses.
Following this beginner’s guide, anyone can successfully grow basil indoors, enjoy a continuous harvest, and benefit from the multiple health, aesthetic, and culinary advantages of this remarkable herb.